Machu Picchu is one of the most iconic landmarks in the world, attracting millions of visitors annually. As one of the New Seven Wonders of the World, it holds a significant place in both history and culture. However, despite its fame, many still find it challenging to locate “Picchu on map” or fully understand its geographical and cultural importance. This article aims to guide you in understanding where Machu Picchu is located, how to find it on a map, and the significance behind this awe-inspiring site.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Machu Picchu?
- Why Is It Called “Picchu” on Map?
- Geographical Location of Machu Picchu
- How to Find Picchu on Map
- Historical Context and Cultural Significance
- Visiting Machu Picchu: Tips and Information
- Comparison Chart: Machu Picchu vs. Other Iconic Ancient Sites
- Conclusion
1. What Is Machu Picchu?
Machu Picchu is an ancient Incan citadel located high in the Andes Mountains in Peru. It was built in the 15th century and later abandoned, only to be rediscovered by Hiram Bingham in 1911. The name “Machu Picchu” itself translates to “Old Peak” in Quechua, the language of the Inca people. While “Picchu” refers to the peak or mountain, “Machu” means old, and it’s the site’s mountainous location that has captivated visitors for centuries.
Machu Picchu is believed to have been a royal estate or a sacred religious site used for astronomical observations, thanks to its alignment with various celestial bodies.
TRENDING:Top Norway News Websites to Follow in 2025 for Accurate and Timely Updates
2. Why Is It Called “Picchu” on Map?
The word “Picchu” is commonly used in the context of Machu Picchu to refer to the peak or mountain that dominates the area. When people search for “Picchu on map,” they are likely looking for the geographical location of this famous site.
It’s important to note that “Picchu” is a generic term that can refer to any mountain or peak in the Andes. However, when used in conjunction with “Machu,” it specifically points to the renowned citadel known worldwide. On a map, “Picchu” marks the topography of the mountains around the site, guiding visitors to the precise area where this majestic landmark lies.
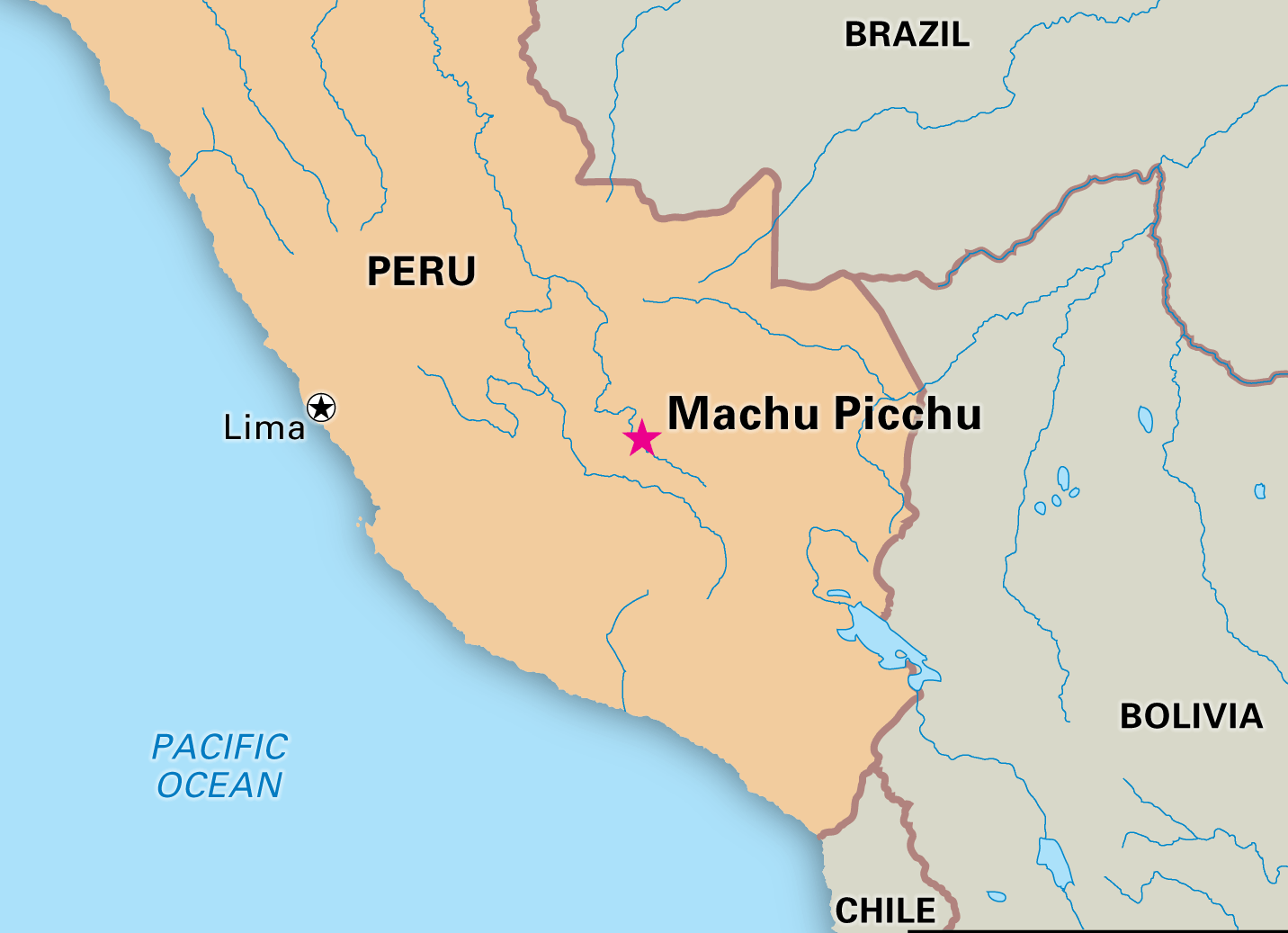
3. Geographical Location of Machu Picchu
Machu Picchu sits at an altitude of 7,970 feet (2,430 meters) above sea level, nestled between the peaks of Machu Picchu Mountain and Huayna Picchu. To find it on a map, it is located in the Cusco Region of Peru, specifically within the Machu Picchu District of the Urubamba Province. The coordinates for Machu Picchu are approximately 13.1631° S latitude and 72.5450° W longitude.
Machu Picchu is accessible from the nearest city, Cusco, which serves as a major hub for travelers. To reach Machu Picchu from Cusco, one can take a train to Aguas Calientes, a town located at the foot of the mountain, and then hike or take a bus up to the ruins.
4. How to Find Picchu on Map
If you’re trying to locate “Picchu on map” digitally or on a physical map, here are the most effective ways:
A. Digital Maps
To find Machu Picchu on digital maps such as Apple Maps, Bing Maps, or other mapping services, simply enter “Machu Picchu” or the coordinates mentioned earlier (13.1631° S, 72.5450° W) into the search bar. This will pinpoint the location with a precise marker, showing you the citadel’s exact position within the Peruvian Andes.
B. Physical Maps
For physical maps, look for the Cusco Region in southern Peru. Machu Picchu will be marked near the town of Aguas Calientes, located to the south of the Urubamba River. Use the high-altitude mountains that surround the site to help guide your way on the map.
C. Google Earth
Google Earth is another useful tool for visually exploring the terrain surrounding Machu Picchu. By zooming into the region, you can get a 3D view of the mountains and terrain, providing an immersive experience of what the landscape looks like from above.
5. Historical Context and Cultural Significance
Machu Picchu is not just a geographical location; it is deeply tied to the history and culture of the Inca civilization. Believed to be built in the mid-1400s under the reign of Inca Emperor Pachacuti, Machu Picchu was a high-altitude city that served as a royal retreat. The purpose of the site remains a subject of debate among scholars. Some believe it was a sacred religious site, while others argue it was a military outpost or a place for astronomical study.
The architectural marvels of Machu Picchu, such as the sophisticated terracing, intricate stonework, and advanced water management systems, demonstrate the exceptional engineering skills of the Inca people. These features have made Machu Picchu an enduring symbol of Incan ingenuity and an important UNESCO World Heritage site.
Moreover, Machu Picchu’s location at such a high altitude likely made it difficult to access, providing a level of security from invaders. Its steep hills, narrow pathways, and hidden location in the mountains would have made it nearly impossible for anyone to approach undetected.
6. Visiting Machu Picchu: Tips and Information
Traveling to Machu Picchu is a once-in-a-lifetime experience for many people. To make the most of your trip, here are some essential tips:
A. Best Time to Visit
The dry season, from May to September, is the best time to visit Machu Picchu. During these months, the weather is relatively dry, making hiking and outdoor activities more pleasant. Avoid visiting during the rainy season (October to April), as trails may become slippery and difficult to navigate.
B. How to Get There
As mentioned earlier, the closest city to Machu Picchu is Cusco. From Cusco, visitors typically take a train ride to Aguas Calientes and then a bus up to the site. Alternatively, some adventurous travelers hike the Inca Trail, a multi-day trek that follows ancient pathways leading to Machu Picchu.
C. Permits and Tickets
Tickets to Machu Picchu are required, and it’s important to book them in advance. The site has strict visitor limits to preserve the site and avoid overcrowding. You can purchase tickets online through the official Machu Picchu website or authorized agents.
D. What to Bring
- Comfortable shoes: The terrain is uneven, so sturdy, waterproof footwear is recommended.
- Sun protection: Bring sunscreen, sunglasses, and a hat to protect yourself from the intense sun.
- Water and snacks: Stay hydrated, especially if you’re hiking.
- Camera: Don’t forget your camera or smartphone to capture the breathtaking views.
7. Comparison Chart: Machu Picchu vs. Other Iconic Ancient Sites
To provide a better understanding of Machu Picchu’s uniqueness, here’s a comparison chart of Machu Picchu and other famous ancient landmarks.
| Feature | Machu Picchu | Great Wall of China | The Pyramids of Giza | Petra, Jordan |
| Location | Peru, South America | China | Egypt | Jordan |
| Built | 15th Century | 7th Century BC | 2580–2560 BC | 5th Century BC to 2nd Century AD |
| Civilization | Inca | Chinese Empire | Ancient Egyptians | Nabataean Arabs |
| Primary Purpose | Religious and royal estate | Defensive fortifications | Tombs for pharaohs | Carved city for trade and religion |
| UNESCO World Heritage | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Visitation Difficulty | Moderate to high (mountain terrain) | Moderate (long stretches) | Low (accessible by foot) | High (requires hiking and climbing) |
| Cultural Significance | Sacred Incan site | Military defense | Ancient Egyptian history | Ancient trade city |
8. Conclusion
Finding “Picchu on map” is more than just locating a geographical location; it’s about discovering a part of the world rich in history, culture, and natural beauty. Machu Picchu is a remarkable site that continues to fascinate historians, travelers, and adventurers alike. Whether you’re planning a trip to Peru or simply intrigued by its story, understanding where Machu Picchu is located and what it represents can enhance your appreciation for this incredible landmark.
Remember, if you plan to visit, always plan ahead by securing tickets and permits well in advance. A visit to Machu Picchu is not just a geographical experience—it’s an immersive journey through time, culture, and the heart of the Andes.